The Effects of Cold and Dry Air on Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be tricky to manage, especially when winter rolls around. The
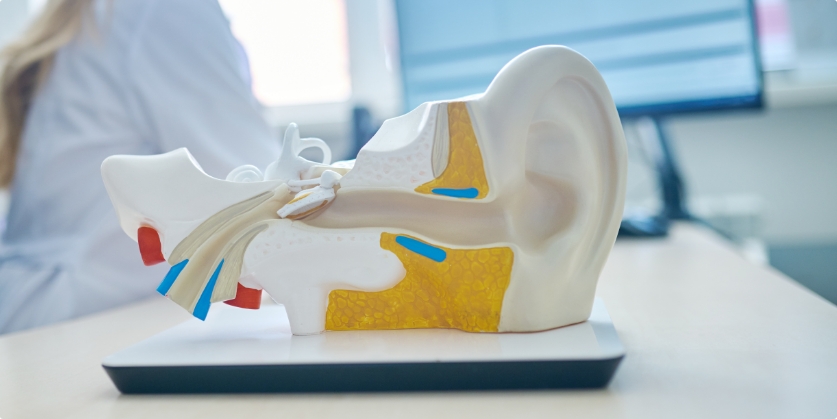

Tinnitus can be tricky to manage, especially when winter rolls around. The

Hearing loss is a common health problem for many, whether it’s something

Attending a hearing specialist appointment for the first time can seem a